HTML 5 Page Layout
The basic structure of a HTML 5 document remains the same. Each HTML 5 page consists of a head section containing unseen elements and links and a body section where the visible elements of the document are present.
HTML offers different tags to build and organize the content in the body of the document. The body structure generates the visible part of the document. One of the elements provided for body is <table> tag. Tables help in improving user’s experience by helping the user to visualize the Web site in an organized manner. Eventually, other elements replaced the function of tables.
These elements have lesser code and are faster, thus facilitating creation, portability, and maintenance of a HTML 5 Web site.
The <div> element was another element that was introduced in this field. With the integration of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and the usage of more interactive applications, the <div> tag was frequently used. Both the <div> and <table> elements, did not
provide information about the sections of the body that the element may be representing. Content such as scripts, images, links, text, menus, forms, and so on could be used between the opening and closing <div> tags.
HTML 5 includes new elements that identity and organize each part of the document body.These elements have lesser code and are faster, thus facilitating creation, portability, and maintenance of a HTML 5 Web site.
The <div> element was another element that was introduced in this field. With the integration of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and the usage of more interactive applications, the <div> tag was frequently used. Both the <div> and <table> elements, did not
provide information about the sections of the body that the element may be representing. Content such as scripts, images, links, text, menus, forms, and so on could be used between the opening and closing <div> tags.
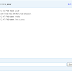
In HTML 5, the most significant sections of a document are separated and marked. Hence, the main structure does not depend on the <div> or <table> tags. A typical HTML page would have a page header, footer, and middle page content. Within the middle page content, at the top level, it may have navigation, content, and aside columns. Also, within the content, more sections can be embedded depending on the page’s specific content.
The Header on the top usually has the logo, name, subtitles, and short descriptions of the Web site or Web page. After that is the Navigation Bar that includes a menu that contains links for navigation. Web users can navigate to different pages or documents using the navigation bar. The most relevant content is generally shown in the middle of the page. The contentpresented in the Main Information part of the layout usually has a top priority. It can have a list of products, description of products, blogs, or any other important information. The Side Bar shows a list of links that lead to certain items that may be present internally on the Web site or on an external link. For example, in a blog, the last column offers a list of links that can lead to the blog entries, information about the author, and so on. These two sections are extremely flexible. Web designers can perform variety of actions, such as inserting more rows or splits the columns, to edit the Web page as required.
The footer at the bottom is used to represent general information about the Web site. This can include the author or the company name, links regarding rules, terms and conditions, location maps, and any other additional data.
The Header on the top usually has the logo, name, subtitles, and short descriptions of the Web site or Web page. After that is the Navigation Bar that includes a menu that contains links for navigation. Web users can navigate to different pages or documents using the navigation bar. The most relevant content is generally shown in the middle of the page. The contentpresented in the Main Information part of the layout usually has a top priority. It can have a list of products, description of products, blogs, or any other important information. The Side Bar shows a list of links that lead to certain items that may be present internally on the Web site or on an external link. For example, in a blog, the last column offers a list of links that can lead to the blog entries, information about the author, and so on. These two sections are extremely flexible. Web designers can perform variety of actions, such as inserting more rows or splits the columns, to edit the Web page as required.
The footer at the bottom is used to represent general information about the Web site. This can include the author or the company name, links regarding rules, terms and conditions, location maps, and any other additional data.
.png)
.png)





.png)